Miami-Dade Advances North Corridor TOD Master Plan with Its First Public Workshop

Miami-Dade’s North Corridor Transit-Oriented Development (TOD) Master Plan is officially moving forward, with its first community workshop scheduled for Wednesday, October 22 at the Sherbondy Village Community Center. The event, which will spam between 6:30 PM to 8 PM, will mark the first of two public workshops aiming to shape future development along Miami’s long-awaited North Corridor. Outlined in 2016 as part of the Strategic Miami Area Rapid Transit (SMART) Program, the North Corridor will extend approximately 10 miles along NW 27th Avenue, from the Dr. Martin Luther King Jr. Metrorail Station to the Broward County line. The goal of the line is to connect residents of unincorporated Miami-Dade, Opa-locka, and Miami Gardens to key destinations such as Miami Dade College, Opa-locka Executive Airport, and Hard Rock Stadium. The development will be one of the First Metrorail extensions in years, following the orange line to Miami International Airport. Among studies for the North Corridor, the county currently lacks a unified plan to guide development around its proposed transit stations. The upcoming workshop, and the planning process that follows, aims to change that. According to Miami-Dade officials, the Master Plan is being drafted to align land use, economic development, and mobility goals alongside the metro extension, ensuring that the region’s growth is sustainable and accessible to surrounding residents. Using a “5D Framework” (Density, Diversity, Design, Destination Accessibility, and Distance to Transit), the plan encourages compact, walkable, mixed-use communities around high-capacity transit. During the drafting process of the TOD Master Plan, planners hope to have a plan that will reduce car dependency and foster safer, healthier neighborhoods that connect people effectively to opportunities. The TOD Master Plan will evaluate land use within a one-mile radius of nine proposed elevated stations, assessing redevelopment potential, infrastructure needs, and pedestrian accessibility. The plan will also define strategies for creating complete streets and transit-ready communities. Progress on the Master Plan will proceed in four phases, with the final plan’s release scheduled for 2026. A second workshop will occur around March of next year. Once completed, the plan will be an additional step for the long-awaited North Corridor, which has been riddled by false promises. Once touted as reaching Hardrock stadium by the World Cup, the transit line is still undergoing funding, studies, and other concerns that have pushed the expected completion date back to 2036. A new Transit-Oriented Development (TOD) Master Plan is viewed as a must for the county, where an increasingly active corridor now demands a guide for growth. Among the projects taking shape is HueHub, a multi-tower complex with buildings rising over 300 FT. Leasing is expected to begin in December, and a new transit station is proposed just 150 feet away.
$60 Million in Federal Funding Killed for Miami’s ‘I-395 Underdeck and Heritage Trail’
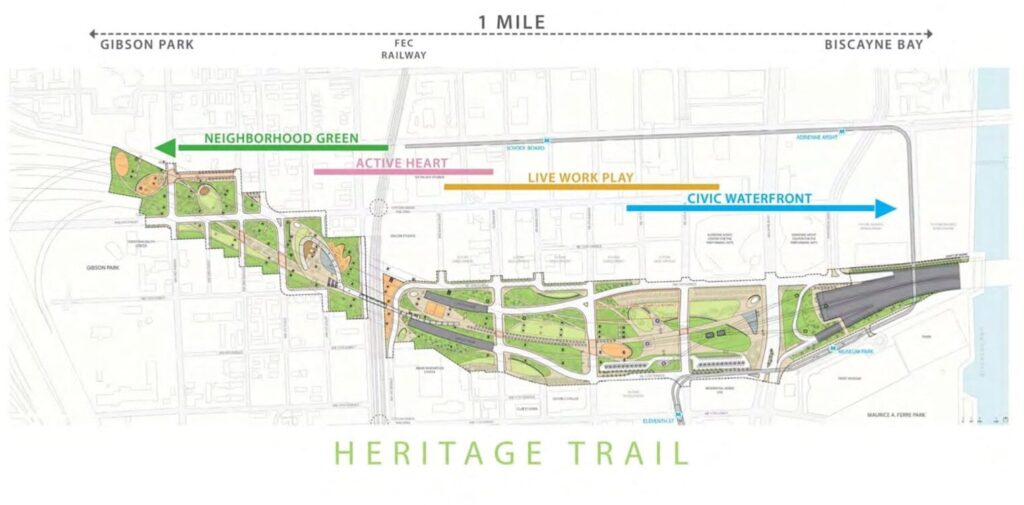
Funding for Miami’s Underdeck and Heritage Trail project has been wiped out. Last week, the city learned that the entire $60 million allocation for the project would be rescinded. The cut originates from the passage of the “One Big Beautiful Bill” in Congress, which eliminated all unobligated funds from the Neighborhood Access and Equity Program: now renamed “Reconnecting Communities.” In Miami’s case, the money was considered unobligated because construction had not officially begun. In a letter provided by Loren Smith Jr, deputy assistant secretary for policy at the DOT, he wrote, “Connecting Miami: I-395 Underdeck and Heritage Trail will undergo and unobligated balance recission of $60,353,730.00”, “H.R. 1, One Big Beautiful Bill” rescinds all unobligated balances from the NAE Program”. The Underdeck was planned as a way to reconnect residents and businesses in Overtown on both sides of the highway, transforming 33 acres into public open space with walking and biking paths, plazas, children’s play areas, water features, spots for food and drink, and so much more. The funding cut couldn’t come at a worse time. Weeks before, news was announced that the Underdeck and Heritage Trail secured the last pieces of financing needed for the project. To unlock the $60.3 million federal grant, the city needed to chip in $10.8 million of its own financing and sign an agreement with FDOT. Earlier this year, $3.8 million from the city was committed, and this week commissioners were approved $3.5 million each from the Omni and SEOPW CRAs, covering the rest of the local share. Together with $11.5 million recently received from FDOT, the project’s total budget was expected to reach about $82.7 million. With the federal funding now off the table, the city will have to find a way to replace the $60 million shortfall before it can even tap into the money already committed by the City of Miami and FDOT. Speaking to the Miami Herald, Commission Chair Christine King, whose district includes the park, said “I am not discouraged”, “If we have to do only a section at a time, that space will be representative of our struggles, our culture, and our resiliency.” Adding to the irony, plans and construction for Miami’s Signature Bridge project, which includes highway upgrades, is still moving forward. Its budget has swelled to $866 million, and the completion date has slipped from fall 2024 to late 2027, and now to late 2029. Far from being just a road improvement project, the bridge features six towering arches that serve both as structural supports and aesthetics. Yet, unlike the Heritage Trail, its funding comes entirely from the State of Florida. However, Miami is not alone. Multiple cities across the U.S. have had funding cut on projects, including Austin. In a similar fashion, Austin’s I-35 cap-and-stitch program lost $105 million in federal funding. The project would’ve delivered above-ground parks and recreation facilities that hid I-35 from public view. Both the Underdeck and the I-35 cap-and-stitch program have one thing in common: both were designed to reduce the harm historically done from highway projects.
Darryl Shaw’s Ybor Harbor Will Soon Call Home to a New Stadium for the Tampa Bay Sun FC
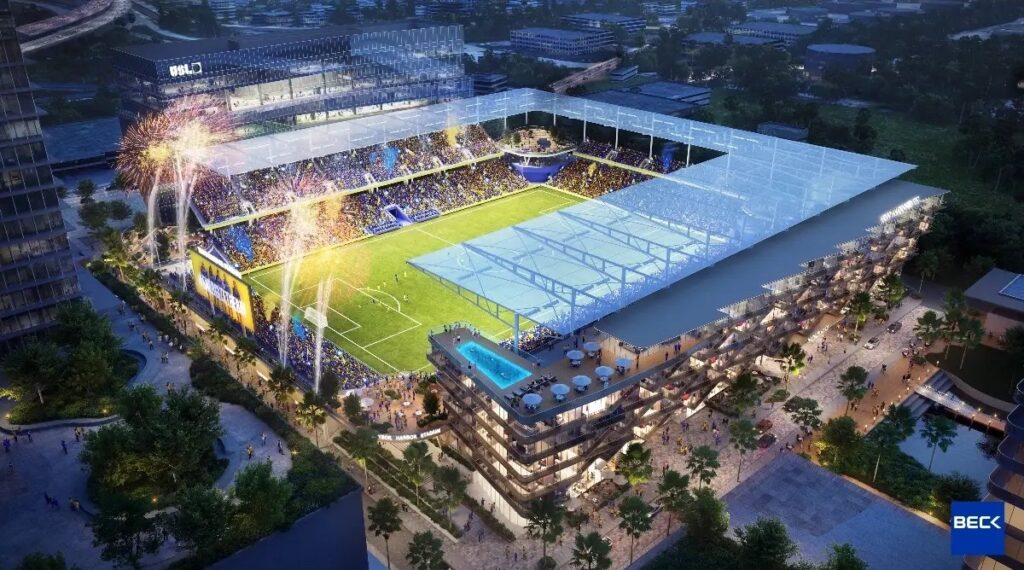

Set between Ybor City and the Port of Tampa, the Ybor Harbor development will soon call home to one of the only soccer stadiums in the U.S. built for a women’s professional soccer team. The 15,000-seat stadium, designed by The Beck Group and spearheaded by Darryl Shaw, is trying to ride the momentum wave of the Tampa Bay Sun’s impressive season, as the team just won the USL Super League’s championship. Women’s soccer in particular is gaining traction across the United States, and the USL along with Darryl Shaw want to be part of the movement. “By collaborating with Darryl Shaw and Tampa Bay Sun FC, we’re accelerating the growth of women’s soccer while creating lasting benefits for Tampa Bay” according to Alec Papadakis, USL Chief Executive Officer. “The growth of women’s soccer” is evident: just a few months ago, the CPKC Stadium in Kansas City became the first soccer stadium “purpose-built for a women’s professional sports team”. The USL, which is already based in Tampa, will soon gain a new state-of-the-art headquarters integrated into the stadium complex. Renderings reveal an office building with direct views overlooking both Ybor Harbor and the stadium itself. Plans also feature a boutique hotel positioned along the waterfront as part of the overall development. Although the stadium’s main purpose is to host women’s soccer, Darryl Shaw has emphasized that it will also serve as a venue for other sporting events, concerts, festivals, and community gatherings. Aside from Amalie Arena, inner-city Tampa lacks a flexible space of this kind, and the new stadium is expected to create a more active community. Ybor Harbor is planned to include over 100,000 SF of open space, and this development emphasizes that priority. Renderings/plans outline large sidewalks, potential retail venues, and greenery that compliment the stadium. Once completed, Ybor Harbor will include 800 hotel rooms, 150,000 SF of street-level retail space, 500,000 SF of office space, and 4,750 residential units with 10% put forth for affordable housing. Ybor Harbor is an ongoing initiative, and while a construction timeline has not been released, it will take some time before the first groundbreaking. What about the Tampa Bay Rays? Although a potential stadium for the team was envisioned in late 2022, documents for Ybor Harbor submitted to City Council in 2023 made no mention of a baseball venue. In fact, incorporating one would require slashing several planned high-rises due to the already tight footprint of the Ybor Harbor site. This update comes as Darryl Shaw recently stated that finding enough land within inner Ybor for a baseball stadium is no longer feasible. Meanwhile, foundation work for multifamily developments, historic restoration, and other construction efforts have been long ongoing in the region. Cost and a construction timeline have not been released, but according to the Tampa Bay Times, the goal may be to develop the Tampa Bay Sun’s stadium through a “public-private” partnership common with recent stadium construction.
First Work on Tampa’s New Green ARTery Begins
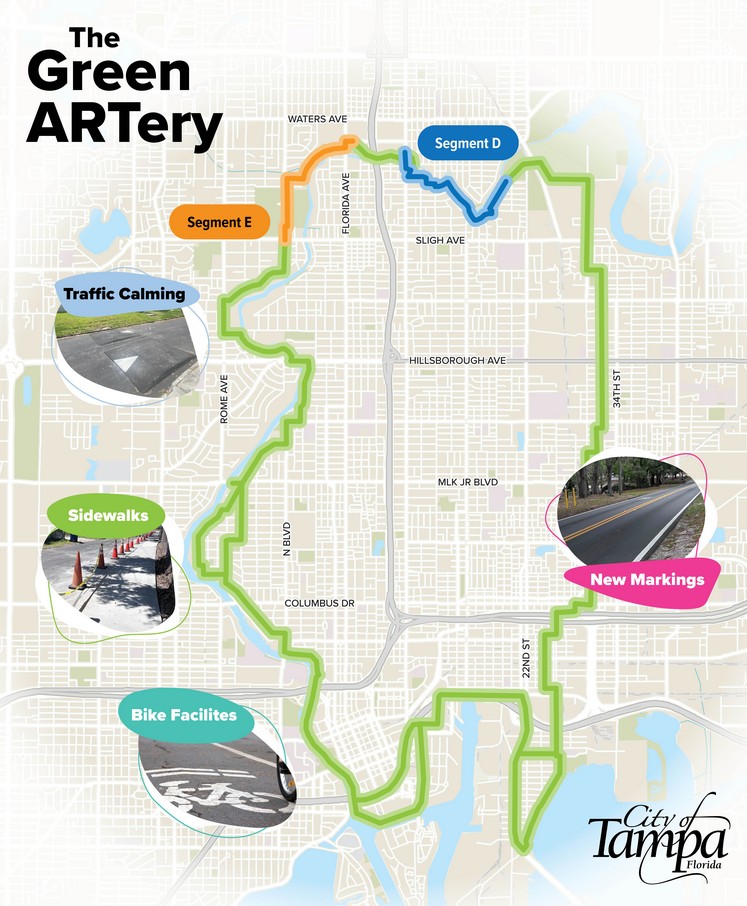
After being proposed in 2010 and undergoing planning for more than half a decade, Tampa’s Green ARTery is beginning its first two segments: Segment D & E. The pedestrian-orientated vision was jump-started in the spring, and involves the construction of an uninterrupted pedestrian-orientated trail where cyclists and pedestrians can enjoy Tampa’s urban landscape under the comfort of traffic calming methods, art, and tree canopies. According to the City of Tampa, residents will see “nearly 4,000 feet of new and widened sidewalks, fresh paving, lower speed limits, solar-powered flashing crosswalk beacons, improved roadway markings, signage, and more.” The first two phases of the initiative will cost around $1.7 million, with half of the funding deriving from FDOT grants and the remainder from multimodal impact fees. Segment E, with an estimated cost of $1,188,166, will link Lowry Park to River Tower Park. The segment will span approximately 1.3 miles and will include widening existing sidewalks, adding new sidewalks with grass buffers, and installing bicycle/pedestrian crossing signage at multiple intersections. According to meetings held during the planning process (which are subject to change), North Boulevard will feature shared lane markings, resurfaced pavement, and reduced speed limits of 25 MPH. Meanwhile, Kirby Street and River Shore Drive will be retrofitted with speed cushions, lower speed limits, a new 5 FT sidewalk with a buffer, and additional improvements. In the final section of segment E, along North Florida Avenue, existing sidewalks will be widened from 5 FT to 8 FT. More information is available at this link: https://www.tampa.gov/project/trans20032. The last segment that began construction is segment D. Despite being at a lower cost of $532,787, the project will actually span more mileage at around 1.4 miles. Like segment E, the project will include “Share the Road” markings, new 5-foot sidewalks, and more. Sidewalks will be provided on the east side of Van Dyke Place and from Hamilton Heath Drive to Hollywood St. Across the entire section includes bicycle boulevard markings and speed cushions on streets such as Park Drive, East Park Circle, and E Patterson St. More information ca be found here: https://www.tampa.gov/project/trans20031. Construction on both segments are estimated to be done by mid-August, while the entire ARTery will be entirely completed by 2030. Throughout the Green ARTery’s phasing, more than 20 neighborhood groups will be involved.
80 Floors in Miami’s Omni District From the Live Local Act? The CITT Annual Workshop Weighs in.
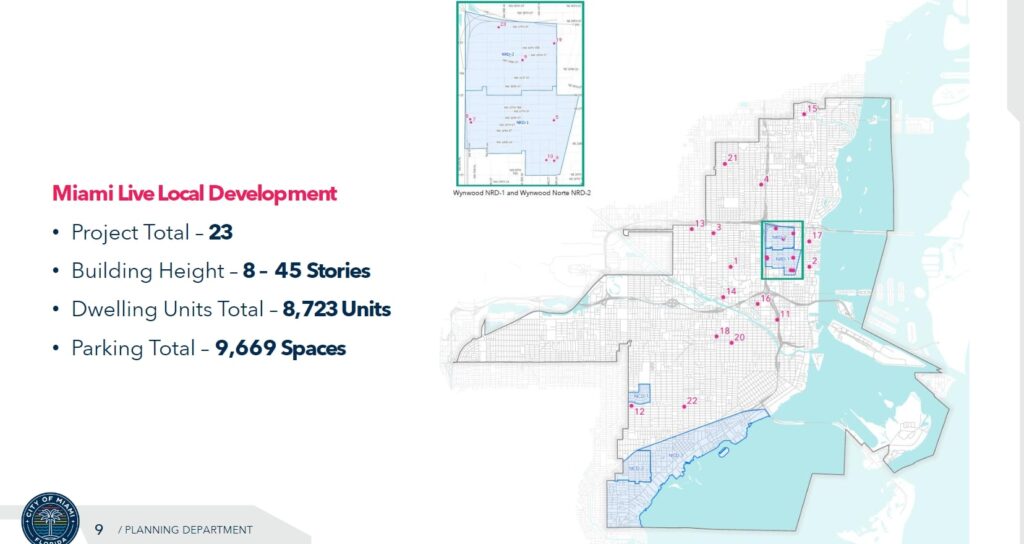
Miami’s long-awaited ‘Citizens Independent Transportation Trust’ held its municipal workshop last month. Attendees discussed a plethora of topics including Miami’s SMART Program, biking networks, and future projections. However, one agenda item stood out the most due to its unique findings: the impact of the Live Local Act on Miami. Background on the Live Local Act The Live Local Act was passed on March 23, 2023 but later updated in 2024. It seeks to supersede local government regulations concerning height, density, and zoning to improve housing costs by streamlining the development of workforce and market-rate housing. This is accomplished by applying the existing zoning from a property located one mile away to the new site. The law has also removed rent control, intending to instead utilize city-owned, commercial, or industrial properties for appropriate workforce housing development. Developers who choose to build upon underutilized land may qualify for expedited building permits, reduced parking requirements, or even tax credits. To qualify, plans must allocate 40% of existing units as affordable and ensure that over 65% of usable square feet is designated for residential use. According to state law, affordable housing is considered to be at 120% of the area median income, which some critics argue is still too high to be really considered ‘affordable’. What Did They Find? A PowerPoint presented last month revealed that Miami currently has 23 Live Local projects already submitted, a number likely to have increased since then. The heights of these projects range from 8 to 45 floors, totaling 8,723 units and 9,669 parking spaces. Most units are clumped near Wynwood and Edgewater, but developments go all the way to city boundaries. A context map taken from Arquitectonica’s 2110 N Miami Avenue presentation shows that large areas in Edgewater and the Omni District are set to benefit from heights of up to 80 floors, with potentially unlimited floors via added benefit heights. Although 80 floors can’t be built due to FAA regulations, neighborhoods such as Overtown and Wynwood will still reap significant advantages, as existing height limits restrict higher development. Even the newly named ‘Wynwood Norte’ neighborhood can see developments rising up to 36 floors with a 24-floor bonus height, with FAA height limits at 500 FT and 450 FT at the end of the neighborhood. From 24 Floors to 80 Floors Take 1361 NE 1 Avenue in the Omni District as an example. Current zoning under ‘Urban Core Transect T6-24‘ permits a maximum height of 24 floors. With the live local act and T6-80 lots (lots that permit 80 floor buildings) less than a mile away, the property now gains from almost unlimited height. Despite the heights being misleading because of FAA regulations allowing a 649 FT maximum height, that still encapsulates about 64 stories which is much higher than any other existing building in the neighborhood. For example, Art Plaza built by the Melo Group is a 32-floor building recently completed in the Omni District using T6-24 zoning. Located less than 50 feet from 1361 NE 1 Avenue, it’s restricted to a maximum height of 24 floors, or up to 48 floors if it meets certain city benefits. This 48-floor limit is considerably lower than the 649-foot height cap permitted by the FAA and the Live Local Act. The Live Local Act ultimately marks a shift away from local governments and conventional zoning, reshaping not just Miami but cities across Florida. Given the prospects of high-rise buildings detailed in this report, community stakeholders need to participate in discussions that balance density with the quality of life. Additionally, the increase in workforce housing alongside a greater housing supply will ultimately help alleviate Miami’s housing crisis.
Miami Beach’s “First Street & South Pointe Stormwater Improvements Project” Progresses to Bring Much Needed Flooding Relief

Miami Beach is continuing their progress on a comprehensive stormwater improvements project in the South of Fifth Neighborhood. The project was recently highlighted in a Hybrid Meeting on November 12, 2024 to discuss the latest developments, along with updates on the project’s development phase. The First Street & South Pointe Stormwater Improvements project originally began when its conceptual layout was proposed in 2022. Since then, multiple public meetings were held to incrementally present the design to the community. The design is now mostly complete, with construction commencement likely happening soon. The goal of the project is to decrease flooding while enhancing the walkability, safety, and aesthetics of the neighborhood. A PowerPoint from April, 2024 highlights such improvements for Washington Avenue and 1st Street. An underground water treatment and pump station will be constructed at the intersection between Washington Avenue and First Street. By the pump station will be a newly-built station for above-ground electrical components, such as a generator in case of power outages. All electrical components will be shielded from the public via an enclosure wrapped in greenery and perforated metal. 1st Street will be entirely reconstructed, both for pedestrian safety and road raising. The road will be raised by around 1.5ft to protect homes and businesses from rising waters, while widened sidewalks and native greenery will be included for expanded pedestrian improvements. As per a graphic from early 2024 that’s likely been updated, the road will be cut to 2 lanes: a 50% reduction from the original amount of lanes. Parking will not significantly reduce for 1st Street or for the adjacent Jefferson Ave. In total, proposed infrastructure improvements include 4 drainage wells, with 2 along Alton road and 2 along Washington Avenue. Pictures below show the improvements done to flooding after construction is completed. Ideally, once all planned South of Fifth Neighborhood upgrades are completed, flooding will cease to exist. The project will begin in 4 phases, with the first phase including the underground pump station for $80M, the second phase constructing improvements for 1st street at $24M, and phase 3 and 4 building improvements to both Washington Avenue and Alton Road at $34M and $40M respectively. The total construction timeline is 51 months, or 4 years and 3 months, with the longest phase being phase 4. Construction on 1st Street will close westbound traffic, though one eastbound lane will remain open during the work.
Tampa’s Green Spine Cycle Track Continues Construction in Ybor
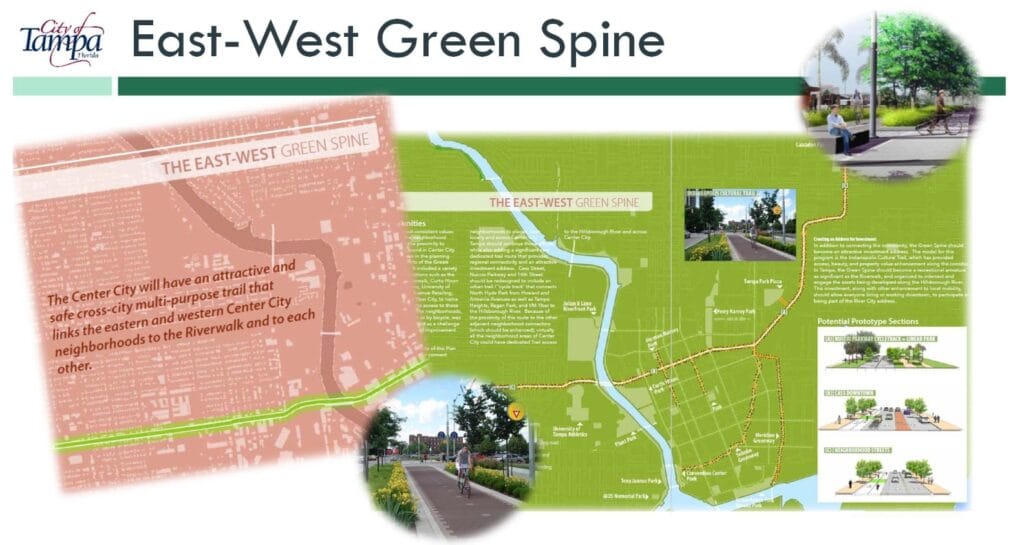
The City of Tampa is moving forward with the next stage of the Green Spine, a bike path that runs from North Hyde Park to V.M. Ybor. The Green Spine was first introduced in the early 2010s as part of the InVision Tampa Center City Plan, aiming to create “an appealing and safe cross-city multi-use trail that connects the eastern and western neighborhoods of Center City to the Riverwalk and to each other.” The entire Green Spine spans 3.4 miles, with the construction for phases 2a, 3a, and 1 already completed. The current phase, phase 3, includes segments 3B and 3C, with a total cost of $1,830,338 for capital improvements. The segment will feature two-lane bike paths with 3-foot concrete buffers, providing better protection for cyclists compared to existing bike lanes in Tampa that use cost-effective flex posts or paint. Construction began in August 2024 and is slated for completion by September of the following year. Recent site photos show that construction on segment 3B (Nuccio Parkway) is already under way, while construction for phase 3C has not yet started. Phase 3C along N 15th St will remove an estimated 42 parking spaces, with 52 remaining. It will develop a connection from Cuscaden Park to North Hyde Park, sparking significant improvements in the neighborhood/surrounding areas ranging from reduced gas consumption, increased tourism, improved water and air quality, and increase community connectivity. To contact the City of Tampa regarding concerns or suggestions, click here for Segment 3C and here for Segment 3B.
Tampa’s TECO Streetcar Has Been Free Since 2018: That May Soon End

Fare-free ridership on the TECO Streetcar Line is quietly coming to an end, ending close to 6 years of free service. The Florida Department of Transportation’s final grant to maintain fare-free service will last until January 5, 2025. The news comes as ridership reaches record highs. A report from July shows that ridership hit 112,999, contributing to around 1.43 million trips in 2024 so far. The Streetcar Line introduced fare-free riding in 2018 thanks to a $2.7 million grant from FDOT, funding the service until 2021. Afterward, an additional grant of $1.4 million was provided to continue the service from 2021 to 2023. Concerns about the end of fare-free ridership resurfaced in 2024. FDOT has committed to a $700,000 grant for this year, but no promises have been made for the future. The team behind Tampa’s TECO Streetcar is working to change that. A Public Hearing on potential fare adjustments is scheduled for November 7, 2024, from 5:30 PM to 7:00 PM, providing opportunities for public comments and survey feedback. The leaders are eager to hear from community members and potentially gather insight into reinstating fare-free ridership. Additionally, seven stations will host Q&A sessions for residents to voice their concerns directly. Fare-Free ridership has been vital for Tampa’s economy. Dense neighborhoods like Tampa’s Water Street District, Channelside, or Ybor, have relied on the streetcar both for tourists and local passenger travel. If fare-free ridership ends, community investment is feared to dwindle. If you’re concerned about fares ending and can’t attend in-person sessions, there’s also an available online survey: TECO Streetcar Survey.
Broward County Transit Operations Facility Revealed in Pompano Beach

Broward County Transit has unveiled redevelopment plans for the COPANS Transit Facility at 3201 W. Copans Road, which currently services as a key operational facility for the county’s bus fleet. The project will involve five buildings, with three existing structures— the refueling building, the bus wash building, and the operations building—being renovated. Planned upgrades to the operations building include a new exterior facade, enhanced CCTV access, and other improvements for departments like IT. Building 1 is set to be demolished to make way for a new 200,000-square-foot maintenance facility. This facility will feature electric bus technology, charging stations, and office space. Its roof will house additional bus charging stations, and the building’s eastern side will include ramps for continuous bus circulation during charging. Solar panels will cover the rooftop, providing an efficient, sustainable, and cost-effective way to charge the buses. A new two-story, 16,900-square-foot training facility will soon be constructed to enhance bus driver training, featuring state-of-the-art driving simulators and in-person learning spaces. As part of this development, the facility’s entrance will see upgrades with proximity card readers, improved guardhouse security, and better access throughout the site. To ensure the property is prepared for future weather events, two on-site lakes and an enhanced drainage system will be added. Additional improvements include expanded bus maintenance parking, pedestrian-friendly pathways, utility upgrades, and fresh landscaping to improve the site’s overall appearance. Spanning approximately 27 acres (or 1.1 million square feet), the property will feature 261,360 square feet of gross industrial space. To accommodate staff and visitors, there will be 514 parking spaces along with 20 bicycle parking spots. In a project narrative, Arcadis, the prime consultant, emphasized that these upgrades reflect ongoing activity and pride in the property’s value to the community. The site is also expected to act as a catalyst for future transit expansions, paving the way for growth in the years to come.
ARCHIVED OPINION | I-395’s Expansion Is Shortsighted
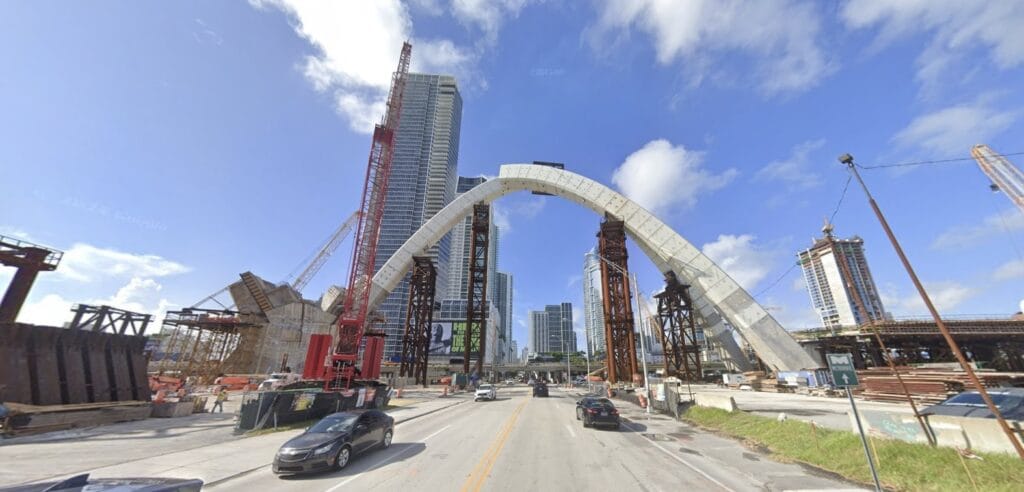

**This article serves as the first opinion piece and is only found in the Transit tab, reflecting the site’s commitment to refining article quality as the format is slowly developed. Miami’s I-395 and Heritage Trail project is being lauded as a groundbreaking initiative aimed to “Restore Connectivity”, “Transform Community”, “Enhance Safety”, “Increase Mobility”, and “Promote Sustainability”. Planners marketed the highway as an escape from the damaging past of I-395, a project that split the historic Overtown neighborhood in two during “Urban Renewal”. Despite polished renderings and vocabulary, the project is a step in the wrong direction for transit improvements in Miami. When the Florida Department of Transportation (FDOT) proposed expansions in the early 2000s, experts began an onslaught of concerns from induced demand, exasperated physical divides, or heightened CO2 emissions. FDOT has disregarded these worries, citing population increases and added vehicular traffic as justification for their nearly billion-dollar investment. In fact, back in the early 2000s, FDOT considered various development options for I-395 including a boulevard, a tunnel, a midtown-roundabout, or a preferred elevated expressway. When Kimley-Horn prepared an assessment of FDOT’s plans for an elevated expressway, they called the idea an “obstacle for redevelopment of the area”, “not an acceptable solution to the City of Miami and the community”, nor does it “have the consensus of entities involved in the decision-making process”. Despite being frowned upon by independent analysis, FDOT continued with their elevated expressway, merely adding decorative arches and a Heritage Trail–a park situated beneath the highway. Even when we give FDOT the benefit of the doubt regarding expansion justifications, a concern remains unaddressed. Initially, FDOT estimated the cost at $545 million (excluding the Heritage Trail) in the 2000s, which then rose to $800 million before rapidly escalating to an $840 million project. This explosive cost is not only unjust to tax payers but also to citizens that rely on mass transportation. Ironically, FDOT’s main goal is to build “a transportation system that not only fits the current needs of Florida’s residents and visitors but also enhances mobility throughout the state to accommodate its consistent and rapid growth.” But, when FDOT solely provides benefits for vehicles over public-transit users, you’re met with low funding and poor planning for projects like Miami’s delayed “North Corridor” Metrorail project. The North Corridor project has been in the works since 1978, aiming to create a Metrorail line leading to Hardrock Stadium. Despite ambitious plans, rising costs and numerous delays prompted Ronald Reagan to famously say, “It would have been a lot cheaper to buy everyone a limousine.” While the statement is illogical, the Metrorail nonetheless only extended to South Miami, leaving the North Corridor sidelined. Voters approved a half-percent sales tax in 2002 to fund the project, but progress remained slow. In 2022, Daniella Levine Cava and Pete Buttigieg highlighted the need for government funding to jump-start the project to meet the upcoming 2026 FIFA World Cup. However, it’s unlikely the 2026 deadline will be met. According to Miami Today, residents should expect to wait until 2036 for the North Corridor to open. Funding is partly to blame for the stalled progress. The $1.9 billion price tag has been challenging to secure. County leaders are optimistic that a combination of sales tax, state, and federal funding will cover the costs for land acquisition and construction. Even so, FDOT has shown over multiple decades to prioritize roadway expansions over public transportation, making funding hard to come by. If history is an indicator, the project will continue to remain stalled amidst design and funding issues while roadway expansions are given millions each year. The North Corridor project serves as a grim example of the failures at state, federal, and local levels to create sufficient mass transportation. While all three entities eagerly await the expansion of I-395, those relying on public transit have been left in the dark for decades. If Miami wants to survive amongst other world-class cities in the world, local and state leaders have an obligation to protect both roadway improvements and mass-transit improvements.